Melisa Docchio
Bats are an important component of Neotropical biodiversity and provide invaluable ecosystem services. Particularly in agroecosystems, insectivorous bats play an important role in arthropod suppression, which may benefit several crops. The role played by insectivorous bats as pest controllers can be valued both ecologically and economically. However, farmers frequently perceive bats as harmful creatures carrying dangerous diseases, and thus, bats are commonly feared and persecuted.
This study attempts to understand and titrate the ecosystem services provided by insectivorous bats in the matrix of agroecosystems and Yungas rain forest in northwest Argentina. It will quantify and communicate among farmers and the whole community the ecosystem service provided by bats as controllers of harmful insects, both for crops and for the human population. The project also aims to raise awareness about the importance of biodiversity for the economy and health of human beings.
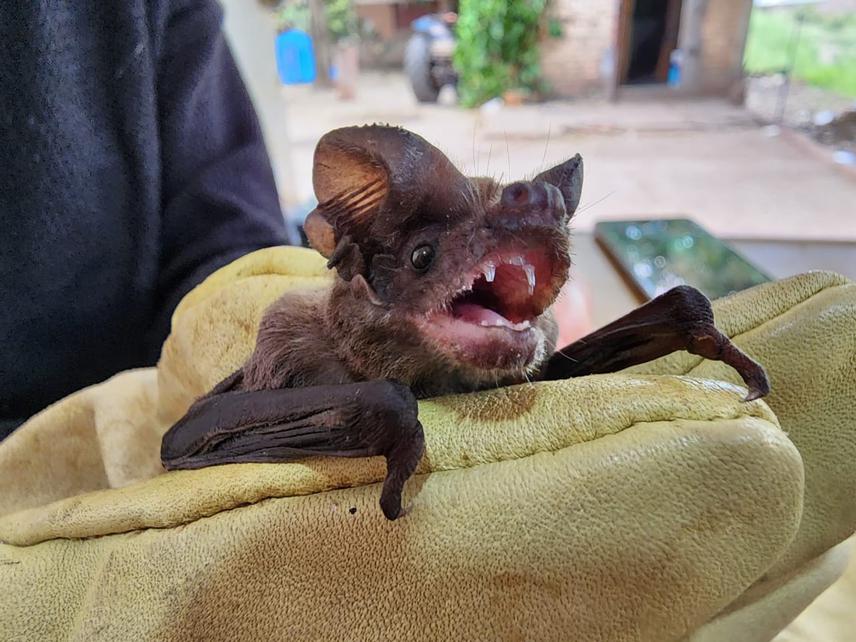
Molossidae Family. ©Melisa Docchio.
Activities
1. To know the perception that the farmers have about the presence of bats in their farms. Based on the results, build, in a participatory manner, a set of simple indicators to be applied by farmers in their farms.
2. To observe the presence, diversity and activity of bats in farms.
3. To evaluate the available insects that bats may consume. I will use light and interception traps for insect sampling.
4. To evaluate the variation of bats diets, I will analyse the faeces obtained from the captured specimens on farms with different management.
5. To analyse the relationship between the indices value and the data on bat diversity and abundance in each of the farms
The project will provide scientific elements that help to change the negative assessment that society has of bats and to preserve the species and populations that inhabit the study area and the entire world. Finally, the information generated by this project will promote the design and management measures for harmonious coexistence between bats and humans, and thus for the conservation of this group. The bat community will benefit, since many bat species do not have sufficient information about their conservation status. In addition, other groups of animals (vertebrates and invertebrates) that cohabit in agroecosystems will benefit.